|
| |
What is Heat Pipe?
|
TTIC Heat Pipe Features: |
- Provide high thermal conductivity with
small temperature difference.
- Fast thermal response.
- Small size and light weight.
- Large variety of shapes.
- No electrical power supply required,
and maintenance free.
- Reduce overall system size and costs.
|
|
TTIC Heat Pipe |
| A efficient heat pipe system
can be afftected by length of a heat pipe, type of fluid in a heat pipe,
return wick type, and the number of bends in a heat pipe.
TTIC
heat pipe technology has been applied to computer cooling for
years. We provide an ideal, cost effective heat pipe solution. Its
small, compact profile and light weight allow it to meeting the
demanding requirements of computer.
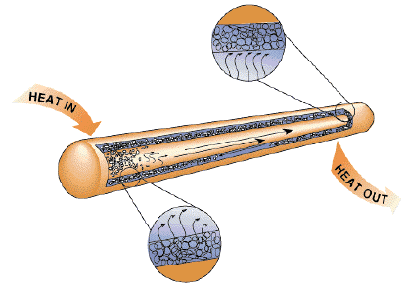
Sintered Powder
This process will provide high power
handling, low temperature gradients and high capillary forces for
anti-gravity applications. The photograph shows a complex sintered wick
with several vapor channels and small arteries to increase the liquid
flow rate. Very tight bends in the heat pipe can be achieved with this
type of structure.
|
|
What's Heat Pipe? |
A heat pipe is a simple
device that can quickly transfer heat from one point to another, which is
usually used for cooling an electronic component in air-conditioners,
refrigerators, heat exchangers, transistors, capacitors, etc. Heat pipes
are also used in laptops to reduce the working temperature for better
efficiency.
 |
|
Heat Pipe Structure: |
A heat pipe is consisting of
following three basic components:
- container
- the wick or capillary.
- the working fluid
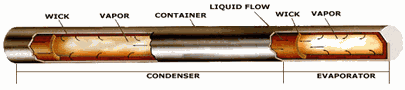
First, the container is a sealed, hollow
tube, which can isolate the working fluid from the outside environment
and can maintain the pressure differential across its walls, and enable
transfer of heat to take place from and into the working fluid. Inside
walls of the container are lined with a porous structure, which is
called capillary structure or wick. The prime purpose of the wick is to
generate capillary pressure to transport the working fluid from the
condenser to the evaporator.Finally, the working fluid is contained in
wick structured container. The first consideration of choosing a
suitable working fluid is the operating vapour temperature range. Most
pipes use water and methanol/alcohol as working fluid. |
|
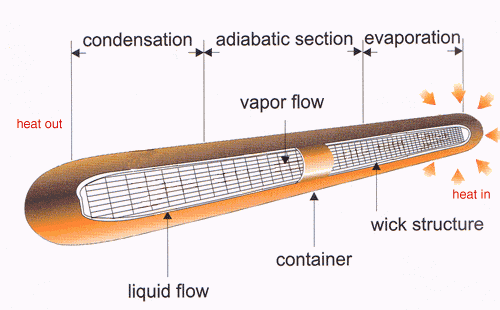
How do Heat Pipes Operate? |
| One end of the heat pipe
attached to the heat source. As the heat rising to the desired operating
temperature, the tube boils the working fluid and turns it into a vapor.
As the evaporating fluid fills the hollow
center of the wick, it spreads throughout the heat pipe toward to the
other cold end. Condensation of the vapor occurs wherever the
temperature is even slightly below that of the evaporation area. As it
condenses, the vapor gives up the heat it acquired during evaporation
and the condensed working fluid is then sucked back to the evaporating
section along the wick structure. This thermodynamic cycle continues and
helps maintain constant temperatures.
Attaching a heat sink to a portion of the
heat pipe makes condensation take place at this point of heat loss and
establishes a vapor flow pattern. Capillary action within the wick
returns the condensate to the evaporator(heat source) and completes the
operating cycle. |
|
Heat Pipe Operating Animation |
 |
|
